The Importance of Monitoring Blood Oxygen Levels for Seniors
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can affect overall health and well-being. One crucial aspect of senior health that often goes unnoticed is blood oxygenation. Oxygen is essential for every cell in the body, and monitoring oxygen levels can help detect underlying health issues before they become serious. For seniors, keeping track of blood oxygen levels is particularly important due to increased risks associated with respiratory diseases, heart conditions, and other chronic illnesses.
Why Blood Oxygenation Matters
Blood oxygenation refers to the level of oxygen present in the bloodstream, typically measured as oxygen saturation (SpO₂). A healthy range for SpO₂ is between 95% and 100%, while levels below 90% can indicate hypoxia, a condition where the body is not receiving enough oxygen. Hypoxia can lead to severe complications, including organ damage and cognitive decline, making it essential for seniors to regularly monitor their oxygen levels.
Early Detection of Respiratory Conditions
Many seniors suffer from respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and asthma. These conditions can cause a gradual decline in lung function, leading to reduced oxygen levels. By monitoring blood oxygenation, seniors and caregivers can detect early signs of respiratory distress, allowing for timely medical intervention. Early treatment can prevent hospitalizations and improve the quality of life for those with chronic lung conditions.
Managing Chronic Illnesses
Seniors are more likely to have chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension, all of which can impact oxygen circulation. Poor oxygenation can strain the heart, making it harder to pump blood efficiently. For individuals with cardiovascular issues, monitoring oxygen levels can help prevent complications such as heart failure and strokes. If oxygen levels drop, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans, including medication changes or supplemental oxygen therapy.
Detecting Silent Hypoxia
One of the most alarming conditions associated with low blood oxygen levels is silent hypoxia, where oxygen levels drop dangerously low without noticeable symptoms. This condition became particularly evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, where many individuals experienced dangerously low SpO₂ levels without feeling shortness of breath. Seniors, who are more vulnerable to infections and immune system complications, should regularly check their oxygen levels to catch silent hypoxia early and seek appropriate medical care.
Cognitive Health and Mental Clarity
Low oxygen levels can have a direct impact on cognitive function. Seniors experiencing chronic low oxygenation may suffer from confusion, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating. Over time, inadequate oxygen supply to the brain can contribute to cognitive decline and increase the risk of conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. By ensuring proper oxygenation, seniors can maintain mental clarity and overall brain health.
Reducing Fatigue and Fall Risks
Fatigue and weakness are common complaints among seniors, but they are often linked to low oxygen levels. When the body doesn’t receive enough oxygen, energy production declines, leading to persistent tiredness and muscle weakness. This can increase the risk of falls, which are a major concern for elderly individuals. Monitoring and maintaining healthy oxygen levels can improve energy levels, mobility, and overall physical health.
Better Sleep and Breathing Disorders
Sleep apnea and other breathing disorders can cause oxygen levels to drop significantly during sleep. Poor nighttime oxygenation can lead to poor sleep quality, morning headaches, and increased daytime drowsiness. If left untreated, conditions like sleep apnea can contribute to heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Seniors who experience disrupted sleep patterns should consider monitoring their oxygen levels at night and consult a doctor if levels frequently drop below normal ranges.
How to Monitor Blood Oxygen Levels
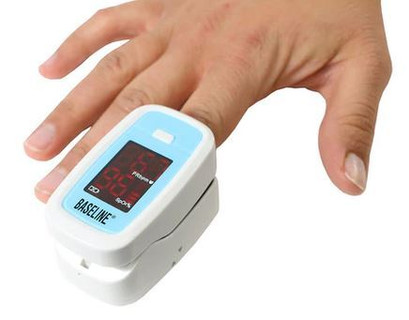
Checking blood oxygen levels is simple and non-invasive. A pulse oximeter, a small device that clips onto the fingertip, provides an easy way to measure SpO₂ levels. These devices are widely available and can be used at home to track oxygen levels regularly. Seniors should take readings when they feel fatigued, short of breath, or unwell. If oxygen levels consistently fall below 90%, medical attention should be sought immediately.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seniors and caregivers should be aware of warning signs that indicate low oxygen levels, including shortness of breath, persistent dizziness, confusion, bluish skin or lips, and rapid heartbeat. If any of these symptoms are present alongside a low SpO₂ reading, emergency medical care may be required. Additionally, seniors with chronic conditions should work with their healthcare providers to establish a routine for monitoring their oxygen levels and managing any fluctuations.
Conclusion
Regular monitoring of blood oxygenation is a simple yet powerful tool for maintaining senior health. By keeping track of SpO₂ levels, seniors can detect potential health issues early, manage chronic conditions more effectively, and improve their overall quality of life. Investing in a pulse oximeter and understanding the significance of oxygen levels can empower seniors and their caregivers to take proactive steps toward better health and longevity. If you or a loved one is at risk for respiratory or cardiovascular issues, consider incorporating oxygen monitoring into your routine for better peace of mind and well-being.
Testing oxygen levels is crucial for seniors. SafeWell Medical Supply has affordable and accurate pulse oximeters so you can know your level in the safety and comfort of your home or anywhere else you may be. Free and fast shipping is our motto. Click on the image or link and order yours today!